Emerging Trends in Digital Marketing for 2024

Introduction The impact of automation on business is transforming the way industries operate. Automation, which uses technology to execute repetitive tasks without human intervention, is reshaping sectors from manufacturing to healthcare. This article delves into the real impact of automation on business and how it influences various industries. Automation in Business: Manufacturing as the Birthplace Manufacturing is a prime example of the impact of automation on business. Henry Ford’s assembly line revolutionized industrial automation in the early 20th century. Today, advanced technologies are further transforming manufacturing. Robots: Modern plants use robotic arms for precision tasks like assembling, painting, and inspecting products. AI & Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms predict machine breakdowns, ensuring timely maintenance and reducing unplanned downtimes. 3D Printing: This technology allows for customization and faster production times, transitioning from prototyping to production. High-Tech Farming: Automation in Agriculture Automation is quietly revolutionizing agriculture, demonstrating another facet of the impact of automation on business. Autonomous Tractors: These self-driving tractors use GPS and sensors to till, plant, and harvest crops. Drones: Drones survey crops, detect diseases, monitor hydration levels, and assist in planting. Smart Irrigation: Automated systems optimize water usage by adjusting based on real-time weather data and soil moisture levels. Precision and Efficiency: Automation in Healthcare Healthcare is a sector where the impact of automation on business is critical, enhancing accuracy and timeliness. Robotic Surgery: Robots like the Da Vinci system enable surgeons to perform procedures with high precision, leading to faster recovery times. AI Diagnostics: AI analyzes diagnostic tests such as X-rays and MRIs, sometimes more accurately than human doctors. Automated Lab Tests: Machines process hundreds of samples simultaneously, delivering faster results. Personalized Shopping Experiences: Automation in Retail The retail industry leverages the impact of automation on business to enhance operations and customer experiences. Chatbots: AI-powered chatbots handle customer inquiries, process returns, and assist in online purchasing. Automated Warehouses: Robots pick, pack, and sort items, exemplified by Amazon’s Kiva robots. Predictive Analytics: AI predicts purchasing trends, helping retailers manage inventory and tailor marketing campaigns. Smarter, Faster Decisions: Automation in Finance Finance is another sector experiencing the profound impact of automation on business. Algorithmic Trading: Algorithms analyze market conditions and execute trades in milliseconds. Robo-Advisors: These platforms provide automated investment advice with minimal human intervention. Fraud Detection: AI systems analyze transactions in real-time to detect and prevent fraudulent activities. Automation in Entertainment: From Creation to Distribution The entertainment industry also feels the impact of automation on business, enhancing creativity and distribution. VFX & Animation: Automation tools create realistic visual effects and animations efficiently. Content Recommendation: Streaming platforms like Netflix use AI to suggest shows and movies based on user preferences. Virtual Reality: Automation in VR production ensures virtual environments respond realistically to user inputs. A Future on Autopilot: Automation in Transportation and Logistics Automation ensures efficient movement of goods and people, illustrating the impact of automation on business. Self-Driving Vehicles: Autonomous vehicles like Tesla’s cars and Waymo’s taxis are redefining transport. Automated Ports: Ports use robotic cranes and AI for cargo handling and sorting. Delivery Drones: Companies like UPS and Amazon experiment with drones for short-distance deliveries. Conclusion The impact of automation on business, driven by AI, robotics, and computing advances, is transforming industries at an unprecedented pace. While it brings productivity and efficiency gains, it also raises concerns about job displacement and workforce retraining. Balancing automation benefits with societal implications is a defining challenge of the coming decades. As industries continue to adopt and adapt to automation, one thing is clear: the world is changing. With these changes, industries are poised to deliver better, faster, and more personalized services and products than ever before.
Beyond the Hype – The Real Impact of Automation on Business

Over the past few decades, automation has become synonymous with progress in various industries. From manufacturing and logistics to customer service and data analysis, businesses are leveraging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and machine learning to automate tasks that were once performed manually. This shift highlights the significant impact of automation on business. Types of Business Automation Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Involves the use of software robots to execute repetitive tasks. AI and Machine Learning: Enables machines to learn from data and make intelligent decisions, reducing the need for human intervention. Internet of Things (IoT): Connects devices and systems to facilitate data exchange and automation in real-time. The Positive Impact of Automation on Business Energy Efficiency: One of the key advantages of business automation is the potential for increased energy efficiency. Automated systems can optimize energy usage by monitoring and adjusting consumption based on real-time data. For instance, smart buildings equipped with automated climate control can reduce energy waste, contributing to a lower carbon footprint. Resource Optimization: Automation allows businesses to optimize resource utilization, minimizing waste and maximizing output. In manufacturing, for example, automated processes can reduce material waste and improve overall resource efficiency. This not only benefits the bottom line but also has positive implications for the environment. Sustainable Supply Chains: Automation plays a crucial role in creating sustainable supply chains. By automating logistics and inventory management, businesses can minimize transportation emissions and reduce excess inventory, leading to a more environmentally friendly operation. Green Technologies: The development and implementation of green technologies are often accelerated by automation. Businesses are investing in eco-friendly solutions powered by automation, such as smart grids, renewable energy management systems, and sustainable production processes. The Negative Impact of Automation on Business Electronic Waste (e-Waste): As businesses embrace automation, the demand for electronic components and devices increases. This can lead to a surge in electronic waste, as obsolete or malfunctioning automated systems are discarded. Proper disposal and recycling of e-waste become critical to mitigate the environmental impact. Initial Carbon Footprint: The manufacturing and deployment of automation technologies contribute to an initial carbon footprint. The production of robots, AI systems, and electronic components involves energy-intensive processes, and the transportation of these technologies to their destination adds to the environmental cost. Job Displacement and Commuting: While not a direct environmental impact, the displacement of human workers due to automation can indirectly contribute to environmental issues. Job displacement may lead to increased commuting distances as workers seek employment opportunities, resulting in higher carbon emissions from transportation. Overreliance on Non-renewable Resources: Some automation technologies rely heavily on non-renewable resources, such as rare earth metals and fossil fuels. The extraction and processing of these resources can have significant environmental consequences, emphasizing the importance of sustainable practices in the development of automation technologies. Navigating the Green Frontier Sustainable Technology Development: Businesses should prioritize the development and implementation of sustainable automation technologies. This includes using eco-friendly materials in manufacturing, reducing energy consumption, and incorporating green design principles. Responsible E-Waste Management: To mitigate the negative impact of electronic waste, companies must adopt responsible e-waste management practices. This includes recycling, refurbishing, and properly disposing of obsolete automation technologies. Energy-Saving Practices: While automation can enhance energy efficiency, businesses should also implement energy-saving practices in their automated systems. This includes optimizing algorithms, using renewable energy sources, and adopting energy-efficient hardware. Workforce Transition and Training: To address the social and environmental challenges posed by job displacement, companies should invest in workforce transition programs and training initiatives. This can help employees acquire new skills and transition into roles that complement automation rather than compete with it. Regulatory Compliance: Governments and regulatory bodies play a crucial role in shaping the environmental impact of business automation. Implementing and enforcing regulations that promote sustainable practices and hold businesses accountable for their environmental footprint is essential. Conclusion The impact of automation on business is a complex and multifaceted issue. While automation offers significant opportunities to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact, it also presents challenges that must be addressed to ensure a sustainable future. By adopting responsible practices, investing in green technologies, and prioritizing environmental stewardship, businesses can navigate the green frontier of automation and contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly world.
The Environmental Impact of Business Automation
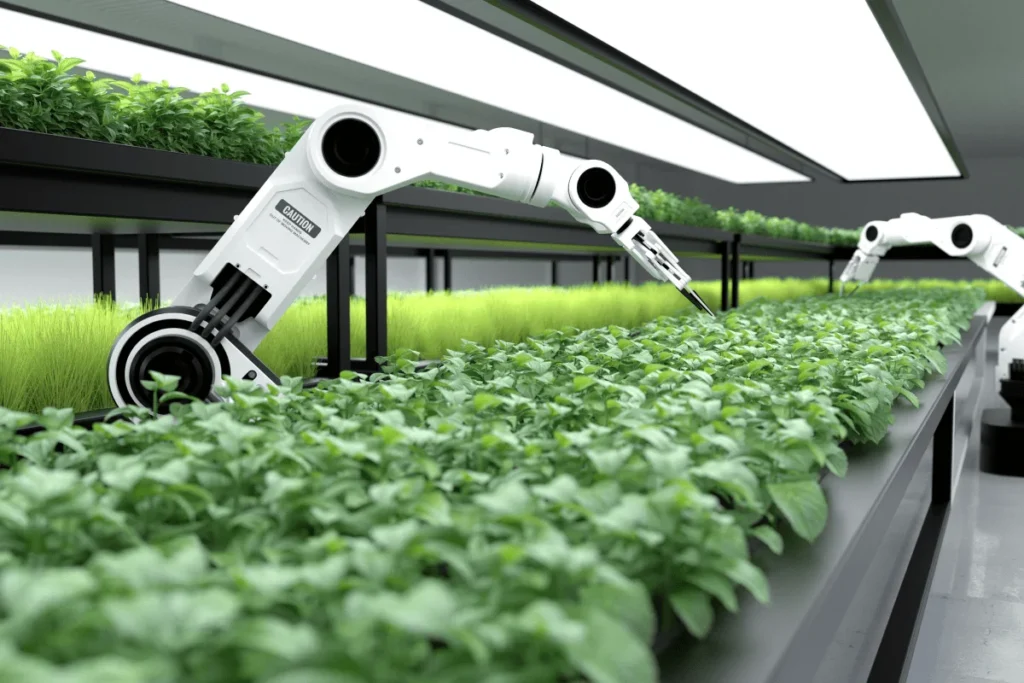

The Rise of Automation Over the past few decades, automation has become synonymous with progress in various industries. From manufacturing and logistics to customer service and data analysis, businesses are leveraging technologies like artificial intelligence (AI), robotics, and machine learning to automate tasks that were once performed manually. This shift highlights the significant environmental impact of business automation. Types of Business Automation Robotic Process Automation (RPA): Involves the use of software robots to execute repetitive tasks. AI and Machine Learning: Enables machines to learn from data and make intelligent decisions, reducing the need for human intervention. Internet of Things (IoT): Connects devices and systems to facilitate data exchange and automation in real-time. The Positive Environmental Impact of Business Automation Energy Efficiency: One of the key advantages of business automation is the potential for increased energy efficiency. Automated systems can optimize energy usage by monitoring and adjusting consumption based on real-time data. For instance, smart buildings equipped with automated climate control can reduce energy waste, contributing to a lower carbon footprint. Resource Optimization: Automation allows businesses to optimize resource utilization, minimizing waste and maximizing output. In manufacturing, for example, automated processes can reduce material waste and improve overall resource efficiency. This not only benefits the bottom line but also has positive implications for the environment. Sustainable Supply Chains: Automation plays a crucial role in creating sustainable supply chains. By automating logistics and inventory management, businesses can minimize transportation emissions and reduce excess inventory, leading to a more environmentally friendly operation. Green Technologies: The development and implementation of green technologies are often accelerated by automation. Businesses are investing in eco-friendly solutions powered by automation, such as smart grids, renewable energy management systems, and sustainable production processes. The Negative Environmental Impact of Business Automation Electronic Waste (e-Waste): As businesses embrace automation, the demand for electronic components and devices increases. This can lead to a surge in electronic waste, as obsolete or malfunctioning automated systems are discarded. Proper disposal and recycling of e-waste become critical to mitigate the environmental impact. Initial Carbon Footprint: The manufacturing and deployment of automation technologies contribute to an initial carbon footprint. The production of robots, AI systems, and electronic components involves energy-intensive processes, and the transportation of these technologies to their destination adds to the environmental cost. Job Displacement and Commuting: While not a direct environmental impact, the displacement of human workers due to automation can indirectly contribute to environmental issues. Job displacement may lead to increased commuting distances as workers seek employment opportunities, resulting in higher carbon emissions from transportation. Overreliance on Non-renewable Resources: Some automation technologies rely heavily on non-renewable resources, such as rare earth metals and fossil fuels. The extraction and processing of these resources can have significant environmental consequences, emphasizing the importance of sustainable practices in the development of automation technologies. Navigating the Green Frontier Sustainable Technology Development: Businesses should prioritize the development and implementation of sustainable automation technologies. This includes using eco-friendly materials in manufacturing, reducing energy consumption, and incorporating green design principles. Responsible E-Waste Management: To mitigate the negative impact of electronic waste, companies must adopt responsible e-waste management practices. This includes recycling, refurbishing, and properly disposing of obsolete automation technologies. Energy-Saving Practices: While automation can enhance energy efficiency, businesses should also implement energy-saving practices in their automated systems. This includes optimizing algorithms, using renewable energy sources, and adopting energy-efficient hardware. Workforce Transition and Training: To address the social and environmental challenges posed by job displacement, companies should invest in workforce transition programs and training initiatives. This can help employees acquire new skills and transition into roles that complement automation rather than compete with it. Regulatory Compliance: Governments and regulatory bodies play a crucial role in shaping the environmental impact of business automation. Implementing and enforcing regulations that promote sustainable practices and hold businesses accountable for their environmental footprint is essential. Conclusion The environmental impact of business automation is a complex and multifaceted issue. While automation offers significant opportunities to improve efficiency and reduce environmental impact, it also presents challenges that must be addressed to ensure a sustainable future. By adopting responsible practices, investing in green technologies, and prioritizing environmental stewardship, businesses can navigate the green frontier of automation and contribute to a more sustainable and eco-friendly world. 4o
The Evolving Landscape of Cyber Threats

The digital landscape is a constantly shifting battleground where cybercriminals employ increasingly sophisticated techniques to exploit vulnerabilities. Traditional security measures, while still valuable, are often reactive and struggle to keep pace with the speed at which threats evolve. This calls for a proactive approach, and automated security emerges as a key player in staying one step ahead of cyber adversaries. Understanding Automated Security Definition and Concepts Automated security involves the use of technology to perform tasks without direct human intervention. From routine processes to complex threat detection algorithms, automation allows for a faster and more consistent response to potential security incidents. Benefits of Automated Security Key Components of Automated Security Systems Threat Intelligence One of the cornerstones of effective automated security is up-to-date threat intelligence. By constantly monitoring global threat landscapes, automated systems can categorize and respond to potential threats with unparalleled accuracy. Incident Response Automated incident response systems streamline the process of identifying, analyzing, and mitigating security incidents. This ensures a rapid and coordinated response, minimizing the impact of a security breach. User Behavior Analytics Understanding normal user behavior is crucial in identifying anomalies that may indicate a security threat. Automation can analyze vast amounts of data to recognize patterns and deviations, triggering alerts for further investigation. Patch Management Keeping software and systems up-to-date is vital for security. Automation can handle the timely deployment of patches and updates, reducing the window of vulnerability. Real-world Applications of Automated Security Network Security Automated systems can monitor network traffic in real-time, identifying suspicious activities and preventing potential breaches. This is particularly critical as businesses increasingly rely on interconnected systems. Endpoint Security Securing individual devices is a fundamental aspect of overall security. Automation helps in the deployment of security updates, antivirus scans, and the isolation of compromised endpoints. Cloud Security As organizations migrate to the cloud, the need for robust cloud security measures becomes paramount. Automation plays a key role in ensuring the continuous monitoring and protection of cloud-based assets, addressing the unique challenges posed by the distributed nature of cloud computing. Overcoming Challenges and Concerns in Automated Security While automation brings numerous advantages, it is essential to address potential challenges and concerns associated with its implementation. The Future of Automated Security As technology continues to advance, the future of automated security looks promising. Integration with cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and predictive analytics is on the horizon. These advancements will further enhance the ability of automated systems to adapt to emerging threats in real-time, ushering in a new era of proactive cybersecurity. Case Studies and Success Stories Examining real-world examples of organizations that have successfully implemented automated security measures provides valuable insights. From financial institutions to healthcare providers, diverse sectors have experienced tangible benefits, including reduced response times, improved threat detection, and overall strengthened security postures. Recommendations for Implementing Automated Security Implementing automated security measures requires a strategic and well-thought-out approach. Here are key recommendations: Conclusion In conclusion, automated security is a cornerstone in the ongoing battle against evolving security threats. By harnessing the power of technology, organizations can fortify their defences, respond swiftly to incidents, and stay one step ahead of cybercriminals. As we navigate an increasingly digital world, embracing automated security is not just an option but a necessity in the pursuit of robust and resilient security measures. The proactive and adaptive nature of automated security positions organizations to not only defend against current threats but also to anticipate and mitigate future challenges. The future of cybersecurity is automated, and those who embrace this paradigm will be better equipped to safeguard their digital assets in the dynamic landscape of cyberspace.
Preparing Your Team for Automation
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, automation is transforming how businesses operate, challenging traditional work notions. As automation technologies advance, organizations must prepare their teams to thrive in this new era. This guide explores strategies and best practices for preparing your team for automation, equipping them with the necessary skills and mindset to navigate automation seamlessly. Understanding Automation and its Impact on the Workforce Before preparing your team for automation, it is crucial to understand what automation entails and its impact on the workforce. Automation uses technology to perform tasks previously carried out by humans. While it can streamline operations, boost efficiency, and reduce human error, it also raises concerns about job displacement and the need for upskilling. Assessing the Current Skill Set of Your Team The first step in preparing your team for automation is assessing the current skill set within your workforce. Understanding team members’ strengths and weaknesses helps identify development areas and essential skills for the automated workplace. Comprehensive skill gap analyses and performance evaluations provide valuable insights into specific areas needing improvement. Identifying Essential Skills for the Automated Workplace Certain skills have become increasingly crucial for success in an automated workplace: Digital Literacy: Proficiency in digital tools and technologies is essential for navigating automated systems. Critical Thinking: Encouraging critical thinking fosters innovation and problem-solving, enabling employees to adapt and identify improvement opportunities. Adaptability: The ability to adapt to new technologies and workflows is critical in an ever-evolving automated environment. Complex Problem Solving: Equipping your team with skills to tackle complex challenges and make data-driven decisions is essential. Implementing Continuous Learning Initiatives Establishing a culture of continuous learning is vital for preparing your team for automation challenges. Encourage participation in training programs, workshops, and online courses to help acquire new skills and stay updated on technological advancements. Providing access to learning resources and creating professional development opportunities empowers your team to adapt to changing demands. Fostering a Culture of Innovation and Collaboration In an automated environment, fostering innovation and collaboration promotes creativity and adaptability. Encourage open communication, idea-sharing, and cross-functional collaboration to facilitate diverse perspectives and ideas. Creating an environment that values experimentation and welcomes constructive feedback stimulates a sense of ownership and engagement among team members. Promoting Emotional Intelligence and Soft Skills Technical skills are essential, but emotional intelligence and soft skills are equally important. Cultivating empathy, effective communication, and interpersonal skills enhances team dynamics and promotes a positive work culture. Encouraging mindfulness practices and work-life balance contributes to overall well-being and resilience, enabling better navigation of automation challenges. Embracing Automation as an Opportunity for Growth Reframe automation as an opportunity for growth and innovation rather than a threat. Communicate the benefits of automation, such as streamlining mundane tasks, enhancing productivity, and creating new opportunities. Encouraging employees to embrace change and participate in implementing automated processes instils a sense of ownership and empowerment. Implementing Change Management Strategies Effectively managing the transition to automation requires robust change management strategies. Communicate the rationale behind adopting automation, address concerns, and provide transparent information about its impact on job roles. Involving employees in decision-making and soliciting their feedback promotes inclusivity and collaboration, ensuring a successful integration of automation. Monitoring and Evaluating the Impact of Automation Continuously monitor and evaluate the impact of automation on your workforce. Analyse key performance indicators, gather employee feedback, and assess the effectiveness of training initiatives to gain insights into your preparation strategies. Adjust your approach based on feedback and proactively address challenges to ensure sustainable growth and development. Conclusion Automation is reshaping the future of work, making it crucial to prepare your team for this transformative shift. By adopting a proactive approach to skill development, fostering continuous learning and collaboration, and viewing automation as an opportunity for growth, you can equip your team to thrive in the automated workplace. Through effective change management and ongoing monitoring, you can ensure a seamless transition and position your team for long-term success in the dynamic digital era.
The Role of Chatbots and Virtual Assistants in Business
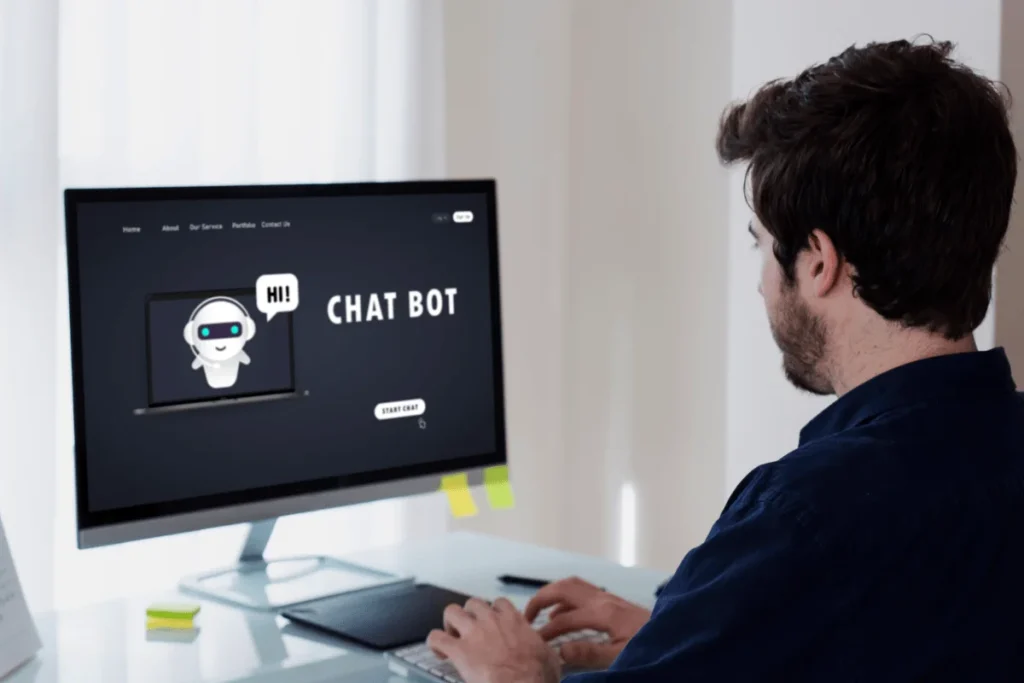

The integration of chatbots and assistants has transformed how businesses operate, communicate with customers, and manage processes. This AI-powered technology enhances customer experiences, streamlines operations, and boosts efficiency. By answering customer queries and automating tasks, chatbots and assistants play a crucial role in modern business. Enhancing Customer Engagement and Support In the digital era, customer engagement and support have become cornerstones of successful business operations. Chatbots and assistants serve as 24/7 customer service representatives, providing instant responses to inquiries and addressing customer concerns promptly. Their ability to understand natural language and provide tailored solutions has revolutionized the way businesses interact with their clientele. Additionally, these AI-driven tools, with personalized responses and quick issue resolution, have significantly boosted customer satisfaction and loyalty. Streamlining Operations and Improving Efficiency Chatbots and assistants optimize internal operations. By automating routine tasks like data entry, scheduling, and troubleshooting, they free employees to focus on complex responsibilities. Integration with software systems enables seamless data management and simplifies workflows, boosting productivity and efficiency. Personalization and Customized Experiences Chatbots and assistants deliver personalized experiences. Through data analysis and machine learning, they understand customer preferences, behavior patterns, and purchase history. This information helps businesses tailor offerings, promotions, and recommendations, creating engaging interactions. Personalization fosters stronger customer relationships, boosts sales, and drives growth. Data Analytics and Insights Chatbots and assistants provide valuable data collection and analysis. By analyzing customer interactions, they offer insights into consumer behavior, preferences, and trends. This data informs business decisions, refines marketing strategies, and aids product development. Leveraging data analytics gives businesses a competitive edge and helps them stay ahead of industry changes. Overcoming Challenges and Ensuring Security Integrating chatbots and assistants presents challenges, especially in data security and privacy. Businesses must implement robust security measures to protect customer information and prevent breaches. Ensuring accurate and reliable chatbot responses is also crucial. Continuous AI algorithm training and improvement are essential. Integration in Various Industries Chatbots and assistants impact multiple industries, including e-commerce, healthcare, banking, and hospitality. In e-commerce, chatbots facilitate seamless online shopping with personalized product recommendations. Meanwhile, in healthcare, they assist with appointment scheduling and patient support. Additionally, in banking, chatbots enable secure transactions, address inquiries, and provide financial advice. Conclusion As technology evolves, chatbots and assistants will expand their role in business operations. These intelligent tools have reshaped customer engagement, streamlined operations, and provided valuable insights. Embracing AI-driven solutions helps businesses adapt to the market, build customer relationships, and drive growth in the digital era.
Automation in Specific Industries

Introduction Automation in business, the use of technology to execute repetitive tasks without human intervention, has transformed the way businesses operate. As industries evolve, there is a growing reliance on machines, algorithms, and sophisticated software to carry out an array of functions that were once done manually. From manufacturing to healthcare, the impact of automation on business is leaving an indelible mark. In this article, we’ll delve into how automation impacts specific industries. Automation in Business: Manufacturing as the Birthplace Manufacturing is arguably the poster child for automation in business. The introduction of the assembly line by Henry Ford in the early 20th century marked the beginning of industrial automation. Today’s factories, however, have gone beyond conveyor belts and simple machinery. Robots: Modern plants boast robotic arms that can assemble, paint, and inspect products with high precision. AI & Predictive Maintenance: AI algorithms predict when machines are likely to break down, ensuring timely maintenance and reducing unplanned downtimes. 3D Printing: This technology has shifted from prototyping to production, allowing for more customization and faster production times. High-Tech Farming: Automation in Agriculture While agriculture may seem like the last place for high-tech automation, it’s undergoing a quiet revolution in business automation. Autonomous Tractors: Self-driving tractors can till, plant, and harvest crops using GPS and onboard sensors. Drones: Used for surveying crops, drones can detect diseases, monitor hydration levels, and even assist in planting. Smart Irrigation: Automated systems can adjust watering based on real-time weather data and soil moisture levels, optimizing water usage. Precision and Efficiency: Automation in Healthcare Healthcare is a critical sector where accuracy and timeliness can be a matter of life and death, making automation in business vital. Robotic Surgery: Robots like the Da Vinci system allow surgeons to perform procedures with unparalleled precision, leading to faster recovery times. AI Diagnostics: AI algorithms can analyze X-rays, MRI images, and other diagnostic tests, sometimes with greater accuracy than human doctors. Automated Lab Tests: Machines can now process hundreds of samples simultaneously, delivering faster results. Personalized Shopping Experiences: Automation in Retail The retail industry is leveraging automation in business to improve both backend operations and customer experiences. Chatbots: These AI-powered entities handle customer inquiries, process returns, and even assist in online purchasing. Automated Warehouses: Robots are used to pick, pack, and sort items. Amazon’s Kiva robots are prime examples of this evolution. Predictive Analytics: Retailers use AI to predict purchasing trends, helping them manage inventory better and tailor marketing campaigns. Smarter, Faster Decisions: Automation in Finance The finance sector relies on quick and accurate data processing, making it ripe for automation in business. Algorithmic Trading: Complex algorithms can analyze market conditions and execute trades in milliseconds. Robo-Advisors: These platforms provide automated investment advice based on algorithms, often with minimal human intervention. Fraud Detection: AI systems can analyze millions of transactions in real-time to detect and prevent fraudulent activities. Automation in Entertainment: From Creation to Distribution The entertainment industry isn’t just about human creativity; automation in business plays a crucial role too. VFX & Animation: Automation tools assist in creating realistic visual effects and animations, saving time and labor. Content Recommendation: Streaming platforms like Netflix use AI to analyze user preferences and suggest shows or movies. Virtual Reality: Automation in VR production ensures that virtual environments respond realistically to user inputs. A Future on Autopilot: Automation in Transportation and Logistics As goods and people move around, automation in business ensures they do so efficiently. Self-Driving Vehicles: From Tesla’s cars to Waymo’s taxis, autonomous vehicles are set to redefine transport. Automated Ports: Ports worldwide are automating their operations, using robotic cranes and AI for cargo handling and sorting. Delivery Drones: Companies like UPS and Amazon are experimenting with drones to make short-distance deliveries. Conclusion The impact of automation on business, driven by advances in AI, robotics, and computing, is transforming industries at an unprecedented pace. While this brings productivity and efficiency gains, it also raises concerns about job displacements and the need for workforce retraining. Balancing the benefits of automation with its societal implications will be one of the defining challenges of the coming decades. As industries continue to adopt and adapt to automation in business, one thing remains clear: the world as we know it is changing. And with these changes, industries are poised to deliver better, faster, and more personalized services and products than ever before.
Scaling with Automation
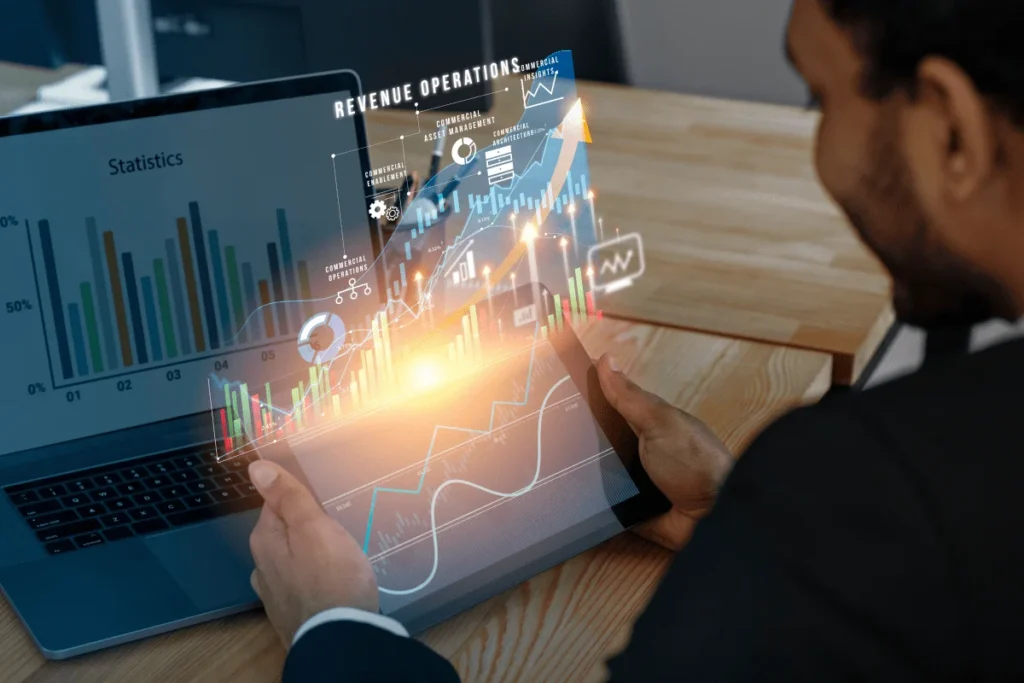

In the era of digital transformation, businesses face the constant challenge of doing more with less. Scaling, which once meant simply adding more employees or investing in additional infrastructure, has evolved. Today, scaling can be achieved with a smaller footprint, thanks to the magic of automation. This post delves into the significance of automation in the scaling process, its benefits, and how businesses can implement it for sustainable growth. What is Automation? In the simplest terms, automation refers to the process of utilizing technology, systems, or algorithms to conduct tasks that were previously performed by humans. These tasks can range from simple ones, like sorting emails, to more complex operations, like manufacturing processes or data analysis. Why is Automation Critical for Scaling? Efficiency and Productivity : Automation allows tasks to be performed faster and more accurately than by human hands. When processes are automated, it eliminates the margin of human error and accelerates the rate of production or service delivery. Cost-Effectiveness : While there might be an upfront cost involved in setting up automated systems, the long-term savings in terms of labor, time, and resources are substantial. Consistency : Automated systems ensure that tasks are performed uniformly every single time, leading to a consistent quality of output. Availability : Automated systems can operate 24/7, ensuring continuous service or production, unlike human employees who require breaks, leaves, and have working hours. Scalability : With automation, scaling doesn’t necessarily mean proportionally increasing resources. You can handle increased demand with the same resources by just optimizing the automated processes. Key Areas Where Automation Aids Scaling Customer Service : Chatbots and Virtual Assistants: With the rise of AI and machine learning, chatbots have become smarter and more intuitive. They can handle a large volume of customer queries simultaneously, offering quick solutions and ensuring customer satisfaction. Marketing : Automated Marketing Campaigns: Tools like HubSpot or Marketo enable businesses to set up automated email campaigns, segment audiences, and even score leads based on interaction, ensuring that marketing efforts are more targeted and effective. Operations : Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA tools can mimic human actions on computer systems. They can handle tasks like data extraction, processing transactions, or even communicating with other digital systems, enhancing operational efficiency. Sales : CRM Systems: Automated CRM systems can track customer interactions, set reminders for follow-ups, and even predict sales trends, helping sales teams manage their pipelines more effectively. Manufacturing : Industrial Automation: From automotive assembly lines to food processing plants, automation has enabled mass production with minimal human intervention, ensuring faster production times and consistent quality. Steps to Implement Automation for Scaling Assess Your Needs : Before diving into automation, identify the areas within your business that require it the most. Which tasks are repetitive? Which processes take up the most time or are prone to errors? Choose the Right Tools : There’s a myriad of automation tools available in the market. Your choice should align with your business needs, budget, and long-term vision. Start Small : Instead of overhauling your entire system, begin with one process. This allows you to monitor results, make necessary adjustments, and ensures a smoother transition. Train Your Team : While automation might reduce the need for human intervention, it’s crucial that your team understands how to work with these new tools. Regular training sessions can help in this transition. Monitor and Optimize : Automation is not a one-time process. As your business grows and evolves, so will your automation needs. Regularly review and optimize your automated processes to ensure they align with your business goals. The Future of Scaling with Automation As technologies like AI, machine learning, and IoT continue to evolve, the potential for automation is limitless. It’s not just about replacing manual tasks but enhancing them to achieve outputs that were previously unimaginable. However, while the allure of automation is undeniable, businesses must approach it judiciously. It’s essential to strike a balance where automation complements human effort rather than replaces it. The future isn’t about machines taking over but about humans and machines working in tandem to achieve unprecedented growth and success. Conclusion Automation is no longer the domain of just the big corporations. Small businesses can, and should, take advantage of the myriad tools available to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and save costs. By starting small, focusing on the right tasks, and maintaining a balance between technology and the human touch, even small businesses can leverage automation without breaking the bank.
Small Business Automation

Introduction In today’s fast-paced digital world, automation in business isn’t just a luxury for the big players—it’s an essential tool for businesses of all sizes. Many small business owners might feel that automation solutions are out of their reach, reserved for corporations with deeper pockets. The reality, however, is different. Small businesses can also leverage the power of automation without breaking the bank. Let’s explore how. Understanding Automation in the Business Context Automation in business, in the simplest terms, is the use of technology to perform tasks without human intervention. In a business context, it can refer to anything from setting up automatic email responses to using sophisticated AI to analyze large datasets. Affordable Automation Tools for Small Businesses Strategies to Implement Automation Effectively Knowing about the tools isn’t enough. It’s crucial to implement them in a manner that brings value to your business: Automation and Customer Relationships One concern many businesses have is that automation might depersonalize their interactions with customers. While there’s some validity to this, it’s all about balance: Identifying Opportunities for Automation Before plunging into the vast ocean of automation tools, it’s essential for businesses to assess their own operations. Data Automation: Small Steps with Big Impacts One often overlooked area, especially in smaller businesses, is data management. Automating data-related tasks can have profound impacts: E-commerce and Automation For small businesses in the e-commerce sector, automation is almost non-negotiable. The Risks and How to Navigate Them While automation can be a boon, it’s not without its pitfalls: Conclusion Automation in business is no longer the domain of just the big corporations. Small businesses can, and should, take advantage of the myriad tools available to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and save costs. By starting small, focusing on the right tasks, and maintaining a balance between technology and the human touch, even small businesses can leverage automation without breaking the bank.
Skills Needed in an Automated Business Landscape

Introduction In the age of rapid technological advancement, automation in business is transforming industries and reshaping the workforce. As machines take over routine tasks, the human workforce must adapt to remain relevant. This shift requires a new set of skills for both employees and employers to thrive in this automated environment. Why is Automation in Business Dominating the World? Automation in business streamlines processes, reduces human errors, and often speeds up production, leading to increased profits. From artificial intelligence to robotics and simple software solutions, automation in business is becoming ubiquitous. However, what does this mean for the workforce? While some fear job losses, the reality is more nuanced. Automation is changing the nature of work, but it’s not eliminating the need for humans. Instead, it’s creating demand for new skills. Key Skills in the Age of Automation in Business Technical Proficiency As businesses adopt more technologies, employees must be comfortable using them. This doesn’t mean everyone needs to become a programmer, but a basic understanding of software and automated tools is beneficial. Data Literacy In an automated business landscape, data is abundant. Understanding how to interpret, analyze, and act on this data is crucial. This skill applies to all roles, from marketing to HR, making data literacy invaluable. Problem Solving and Critical Thinking Automation handles routine tasks, leaving humans to tackle complex issues. Employees with the ability to think critically, identify problems, and formulate solutions will be highly valued. Creativity Machines are logical, but they lack imagination. The human ability to think outside the box, innovate, and bring unique perspectives is essential, especially in industries like marketing, design, and content creation. Emotional Intelligence (EI) In a world dominated by machines, human connection becomes even more critical. EI involves recognizing and understanding emotions, enabling effective communication and collaboration. Adaptability and Lifelong Learning The pace of technological advancement means that today’s tools and methods may be obsolete tomorrow. An eagerness to learn and adapt is a must. Collaboration As tasks become more complex, cross-functional collaboration becomes essential. Effective teamwork and communication skills are vital. Leadership and People Management Even with automation, human teams need guidance. Leadership in an automated world is about inspiration, direction, and fostering a culture of continuous learning. Sales and Negotiation Machines can handle data, but the art of persuasion and building relationships remains a human domain. This skill will always be in demand. Ethical Judgment As businesses use more automation and AI, ethical dilemmas arise. Making the right call requires a deep understanding of societal values and moral principles. Prepping for the Future of Automation in Business As automation in business becomes more prevalent, continuous learning is essential. Here are some steps to stay relevant: Enhancing Soft Skills in an Automated Era With machines handling quantitative tasks, qualitative aspects of business gain prominence. Hone the following soft skills: Tools and Resources to Stay Ahead Several tools and platforms can help professionals stay updated: The Human-Machine Partnership in Business The future is about humans and machines working in tandem. Here’s how to foster this partnership: Conclusion Automation in business is not a threat; it’s an opportunity. The business landscape is evolving, and so must the skills of the workforce. By focusing on continuous learning and embracing the new paradigm, professionals can ensure they remain indispensable in an automated business world.
